Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Program Overview
Combined Heat and Power, also referred to as cogeneration, is the simultaneous generation of useful heat and electricity from a single fuel source. Most often, heat created during power generation (for example, steam generated to run a turbine) is reused for another activity (such as warming a greenhouse or facilitating a chemical reaction) instead of being vented or radiated to the environment. This transformation of a waste product into a useable input increases the efficiency of the fuel source. Employed strategically, CHP can improve the efficiency of facilities and help reduce statewide GHG emissions.
The CPUC supports the deployment of CHP, recognizing the potential contributions CHP can make to the state's energy needs and greenhouse gas mitigation objectives.
CPUC’s Qualifying Facilities and Combined Heat and Power Program
The CPUC administers a Qualifying Facilities and Combined Heat and Power Program. Qualifying facilities are CHP facilities that meet certain size and efficiency criteria. Qualifying facilities can sell the energy they generate to investor-owned utilities (IOUs) at predetermined prices and conditions. See the CHP Procurement page for more details on prices and contracts.
CPUC’s program follows Commission Decision (D.)10-12-035, which adopted a Settlement for Qualifying Facilities and Combined Heat and Power (QF/CHP Settlement). The QF/CHP Settlement was the result of an 18 month-long negotiation between the investor-owned utilities, CHP trade representatives, and ratepayer advocacy groups to clarify state and utility obligations under the federal 1978 Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act (PURPA). The QF/CHP Settlement:
- Created a new state-administered QF/CHP Program;
- Provided a roadmap for a smooth transition from the existing federal jurisdiction standard-offer pricing model program to a procurement program under state jurisdiction using a market-based approach for pricing; and
- Resolved ongoing CHP litigation.
Today, California’s QF/CHP Program focuses on delivering CHP benefits and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reductions. CHP-related regulatory documents are available in the 'Decisions and Other CPUC Documents' and 'QF/CHP Facility-related Documents' sections below.
CPUC’s QF/CHP Program, which implements the QF/CHP Settlement, requires that:
- California’s three largest Investor-owned utilities (Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E), San Diego Gas and Electric Company (SDG&E) and Southern California Edison Company (SCE)) collectively procure 3,000 megawatts (MW) of capacity from CHP facilities by 2018, and
- Reduce GHG emissions by 2.72 Million Metric Tonnes (MMT) by 2020.
These goals were designed to preserve energy resource diversity, fuel efficiency, provide GHG emissions reductions, and promote new, lower GHG-emitting CHP facilities while encouraging repowering, operations changes through utility pre-scheduling, or retirement of existing high GHG-emitting CHP facilities.
Progress toward the MW and GHG goals is tracked via QF/CHP Program Semi-Annual Reports IOUs submit to CPUC’s Energy Division. Links to download reports are provided in the ‘Reporting’ section below.
Progress Toward Procurement Targets
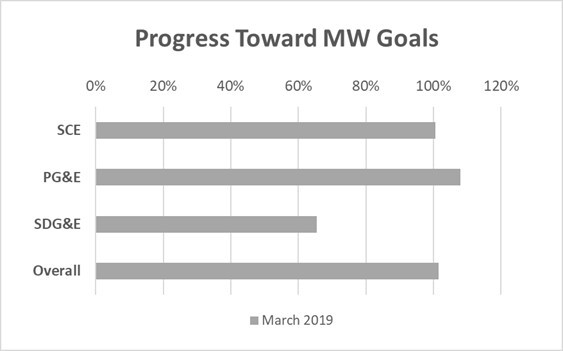
The QF/CHP Settlement required procurement of 3,000 MW of CHP capacity by 2018. Responsibility to meet this goal was distributed among California’s three largest IOUs. The table below summarizes each utility’s obligations and their current progress.
|
Utility |
Settlement Target (MW) |
Current Procured (MW)* |
Percent Toward Target |
|
SCE |
1,402 |
1,409 |
100% |
|
PG&E |
1,387 |
1,497 |
108% |
|
SDG&E |
211 |
138 |
65% |
|
Overall |
3,000 |
3,044 |
101% |
*As of March, 2019.
The QF/CHP Settlement also required California’s three largest IOUs to reduce GHG emissions by 4.82 Million Metric Tonnes (MMT) by 2020, consistent with targets in the 2008 California Air Resources Board scoping plan. This goal was modified later by CPUC in 2015’s Decision 15-06-028 to 2.72** MMT to:
- Better balance the goals of stimulating CHP procurement and the cost-effective achievement of long-term statewide emission reductions; and
- Align targets with more realistic assumptions that reflect current (post 2008) state policies.
**Closing of existing CHP facilities during the Initial Program Period resulted in a net GHG debit of 0.023 MMT, per the Settlement terms. In August 2016, this debit was distributed to the IOUs based on each IOU's share of the California Energy Commission published retail sales, pursuant to Term Sheet Section 6.4.4, increasing the D.15-06-028 combined goal to 2.743 MMT (reflected in the table below).
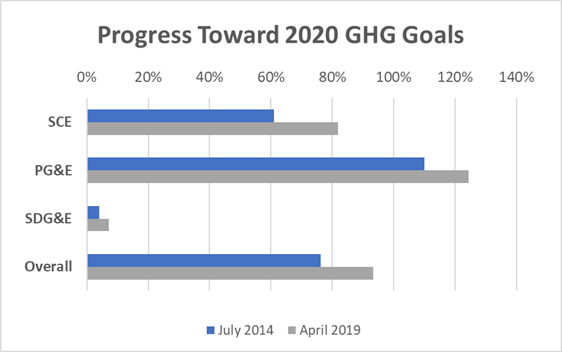
The table below summarizes each utility’s GHG emission reduction obligations and their current progress. The target for each IOU was based on the volume of the individual IOU’s retail sales from bundled and unbundled customers within their service territories.
|
2020 GHG Emission Reduction Targets |
|||||
|
Utility |
GHG Reduction Goal (MMT) |
Progress as of 2014 (MMT) |
Percent Toward Target |
Progress as of 2019 (MMT) |
Percent Toward Target |
|
SCE |
1.23 |
0.74 |
61% |
1.01 |
82% |
|
PG&E*** |
1.23 |
1.34 |
110% |
1.53 |
124% |
|
SDG&E |
0.283 |
0.01 |
4% |
0.02 |
7% |
|
Overall |
2.74 |
2.09 |
76% |
2.56 |
93% |
***GHG reduction targets were revised in June 2015’s D.15-06-028. PG&E’s original target (Established in December 2010’s D.10-12-035) was 2.17 MMT. PG&E’s procurement as of July 2014 to meet their original goal exceeded the June 2015 revised goal.
Reporting
Two data sources for additional information on IOU use of CHP facilities are available to the public:
(1) CHP Program Semi-Annual Reports
Each report has aggregated information on the IOUs' CHP procurement and data on how individual projects contribute to the IOUs' MW and GHG reduction targets under the QF/CHP Settlement. Each successive report provides cumulative information on the IOUs' CHP resources.
The CHP Reporting Template (Version 3.3.3) is also available for download. Reported facilities in the template file are fictitious and are provided for demonstrative use only.
Download Links
CHP Reporting Template V 3.3.3 Download Here
Filed Semi-Annual Reports Download Here
(2) Qualifying Facility Reports
These reports contain information on each utility’s Qualifying Facilities under the Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act (PURPA), which include CHP (cogeneration) facilities as well as other forms of small, renewable energy resources that are not part of CPUC’s QF/CHP Program.
Decisions and Other CPUC Documents
The following Decisions and docket cards correspond with important points in the development of CPUC's Combined Heat and Power Program. Decisions are formatted: D.Year-Month-Index Number.
- D.10-12-035: Adopted a comprehensive Settlement for Qualifying Facilities and Combined Heat and Power (QF/CHP Settlement).
- D.11-03-051: Denied a motion for a rehearing of D.10-12-035 and made minor modifications to D.10-12-035.
- D.11-04-033: Provides a full procedural history and history of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) filings related to IOU use of CHP in California.
- D.11-07-010: Grants a petition to modify D.10-12-035 and made minor modifications to D.10-12-035 relating to treatment of Municipal Departing Load customers.
- D.14-10-046: Approved a SoCalGas pilot for bottoming cycle CHP.
- D.15-06-028: Modified IOU GHG Reduction Targets.
- D.15-10-049: Established a Distributed Energy Resources Services (DERS) Tariff by which Southern California Gas Company may facilitate the adoption and use of combined heat and power (CHP) energy systems for its customers.
- A.08-11-001: Consolidated QF/CHP Docket Card (closed)
QF/CHP Facility-related Documents
Each link in the table below reflects an agreement or action between an IOU and a specific CHP facility or facilities. These actions were taken to fulfill IOU requirements pursuant to the QF/CHP Settlement and approved by CPUC. Some types of IOU/CHP facility agreements do not require approval by the CPUC on a case-by-case basis (for example, facilities using the AB 1613 FiT) and are not included in the table below.
Additional information on procurement from CHP facilities can be found on CPUC’s CHP Procurement page.
|
Decisions and Resolutions pursuant to the QF/CHP Settlement |
|
|
2011 |
|
|
PG&E |
E-4412 (Pacific Oroville) E-4427 and per AL 4336-E (DG Fairhaven) D.11-03-011 (High Sierra Limited, Double C Limited, and Kern Front Limited) D. 11-06-029 (Yuba City Cogen, Greenleaf 1, and KES Kingsburg) E-4413 (Berry Petroleum) |
|
SCE |
E-4443 (Fixed Energy Price Amendments) |
|
2012 |
|
|
PG&E |
E-4452 (Pacific Oroville) E-4485 (Collins Pine) E-4478 and per AL 4335-E (Honey Lake) E-4491 (Burney Forest) D. 10-04-028 modified by D. 12-04-011 (CSU East Bay Fuel Cell) D.11-03-010 (Mid-Set Cogen Co, Coalinga Cogen, Salinas River Cogen, and Sargent Canyon Cogen AL 4033-E (Badger Creek, Berry Petroleum, Chalk Cliff Limited, Forward Power Plant, Graphic Packing International, Live Oak Limited - McKittrick Limited and Plains Exploration) AL 4132-E (Western Power and Steam, Aera Energy, LLC (South Belridge)) Frito-Lay and Berry Petroleum E-4494 (O.L.S. Energy - Agnews) |
|
SCE |
E-4490 (Fixed Energy Price Amendments) E-4537 (Watson) D. 10-04-028 modified by D. 12-04-011 (San Bernardino Fuel Cell) |
|
2013 |
|
|
PG&E |
E-4528 and E-4578 (Bailey Creek Hydro QF) E-4529 (Los Medanos) modified by AL 4275-E E-4594 (Kern River) E-4581 (Oroville Cogen) |
|
SCE |
E-4553 (Berry Newhall) E-4571 (Kern River and Sycamore) E-4569 (Los Medanos and Gilroy) E-4554 (Harbor) – Denied by CPUC E-4555 (Sycamore) |
|
2014 |
|
|
PG&E |
AL 4409-E; E-4409-E-A; 4409-E-B (Ripon Generation) E-4661 (Midway Sunset) E-4632 (Sierra Pacific Industries - Anderson II, Burney, Lincoln, Quincy, and Sonora) E-4648 (Chevron Richmond) E-4662 (ArcLight - Badger Creek Limited, Bear Mountain Limited, Chalk Cliff Limited, Live Oak Limited, and McKittrick Limited) |
|
SCE |
D.14-07-019 (El Segundo) |
|
SDG&E |
E-4642 (CP Kelco) E-4698 as modified by D.15-05-033 (Goal Line) AL 2674-E (Yuma Cogeneration Associates) |
|
2015 |
|
|
PG&E |
D.15-02-019 (Rio Bravo Poso) 4731-E and 4731-E-A (Western Power and Steam, Inc.) 4626-E Chevron U.S.A. (McKittrick) E-4702 (Burney Forest) modified by AL 4706-E AL 4489-E (Tesoro Martinez) |
|
SCE |
E-4681 (Berry University, U.S. Borax, New-Indy Ontario, New-Indy Oxnard) E-4682 (Elk Hills Power) E-4710 (ACE) E-4714 (Watson) AL 3234-E (Rio Bravo Jasmin) |
|
2017 |
|
|
PG&E |
AL 5171-E (Berkeley Cogen) |
|
SCE |
E-4800 (Tesoro) E-4860 (OLS Energy-Chino) |
|
SDG&E |
E-4799 (CP Kelco, U.S., Inc.) |
|
2018 |
|
|
SCE |
E-4911 (VIAS Energies, Inc.) E-4925 (Carson Cogeneration) E-4953 (Corona Energy) E-4957 (CSU Channel Islands / CI Cogen) AL-3882-E (Proctor & Gamble - Oxnard) AL 3700-E (Midway Ventures) – Denied by CPUC. |
|
SDG&E |
E-4901 (AEI) |
Quick Links
- IOU pages on the QF/CHP Settlement
- California Energy Commission CHP website
