Greenhouse Gas Cap-and-Invest Program
California's Greenhouse Gas Cap-and-Invest Program helps to fight climate change by reducing California's greenhouse gas pollution. Originally named Cap-and-Trade, the Cap-and-Invest Program was designed by the California Air Resources Board (CARB) to achieve the goals of the Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006 (AB 32). It creates incentives for our utilities and industries throughout the state to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions, improve the efficiency of their operations, and move toward cleaner forms of energy.
The CPUC directs investor-owned utilities (like PG&E, SCE, SDG&E, and SoCalGas) to distribute funds generated by the Cap-and-Invest Program as credits to residential customers, small businesses, industry, and for clean energy and energy efficiency programs. Program achievements include:
- Distributed over $19.4 billion of Cap-and-Trade funds to residential households, small businesses, and industry since 2014.
- Each year over 11 million households receive the electric California Climate Credit and over 12 million households receive the natural gas California Climate Credit.
- Over $1 billion in Cap-and-Invest program funding available to improve access to solar and clean energy technologies in disadvantaged communities.
Cap-and-Invest Overview
To slow climate change we must steadily decrease the amount of greenhouse gases we release into the atmosphere each year. One way to do this is to limit the total amount of greenhouse gases that can be emitted in California, and then to lower that limit each year. The California Air Resources Board (CARB)’s Cap-and-Invest Program takes that approach: it set a statewide greenhouse gas emissions cap, and each year it will lower the cap until California reaches its emissions reduction goals.
Cap-and-Invest was designed by CARB to achieve the goals of the Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006 (AB 32) - including reducing California's greenhouse gas emissions to 1990 levels by 2020 - and the goals of AB 398, which clarified the role of California's Cap-and-Invest Program in achieving California's 2030 greenhouse gas emissions target of 40 percent below 1990 levels.
The Cap-and-Invest Program encourages electricity providers to shift toward clean sources of energy - the kind that comes from wind, solar, geothermal, and other renewable resources.
Under CARB's regulations, electricity companies that import or supply electricity from non-renewable sources must purchase permits (known as allowances or offsets) for the greenhouse gas emissions that come from burning fuel to make this electricity. These pollution costs are reflected in all customers' electricity rates - specifically in the portion of electricity bills that represents the costs to generate electricity. When natural gas utilities sell to customers, they must pay for emissions associated with customer burning of these fuels and pass these costs on through customers' bills in their gas transportation rates.
Find out more about the Cap-and-Invest Program on CARB’s website.
CPUC's Role
As regulators of the state’s electric and natural gas utilities, the CPUC plays several important roles in implementing parts of the Cap-and-Invest Program. The utilities are major participants in the Cap-and-Invest Program, and CPUC oversees how they comply with CARB's greenhouse gas emissions requirements. CPUC decides how to use some of the proceeds generated from the program to benefit utility customers. CPUC also ensures that the Cap-and-Invest-related costs utilities include in electric and natural gas rates are fair and reasonable.
To learn more and to participate in our decision-making process, read about our relevant proceedings.
Funds to Protect Customers
Power plants, natural gas utilities, and other large industrial facilities must pay when they put greenhouse gas emissions into the air. Some of that money is used by California to fight climate change, and some goes to customers. Community choice aggregator (CCA), direct access, and bundled customers are all treated equally when distributing credits from Cap-and-Invest Program funds.
For electric investor-owned utility customers:
- Residential California Climate Credit.
Households receive a California Climate Credit twice a year on their electric bill. Learn how much your electric California Climate Credit will be. - Small Business California Climate Credit.
Small businesses receive a twice-annual California Climate Credit on their electric bill. - CA Industry Assistance.
At-risk industrial facilities receive a credit once per year. Learn more about CA Industry Assistance. - Clean Energy and Energy Efficiency Projects
CPUC directs some funding to support access to solar and other clean-energy technologies to disadvantaged communities through programs like the Solar on Multifamily Affordable Housing (SOMAH) program.
For natural gas investor-owned utility customers:
- Residential California Climate Credit
Households receive a California Climate Credit once a year in April. Learn how much your natural gas California Climate will be. - Building Decarbonization Pilot Projects
Starting in 2020, CPUC will direct $200 million in funds over four years to the Building Initiative for Low-emissions Development (BUILD) Program and the Technology and Equipment for Clean Heating (TECH) Initiative.
Assistance Totals
CPUC directs electric and natural gas investor-owned utilities to distribute the majority of their Cap-and-Invest Program proceeds backs to residential customers. Since 2014, households have received over $17 billion in credits on their electric and natural gas utility bills. On top of that, CPUC has also directed investor-owned utilities to provide over $2 billion to California businesses to help incentivize efficient production of goods and services in California through the California Industry Assistance and Small Business California Climate Credits.
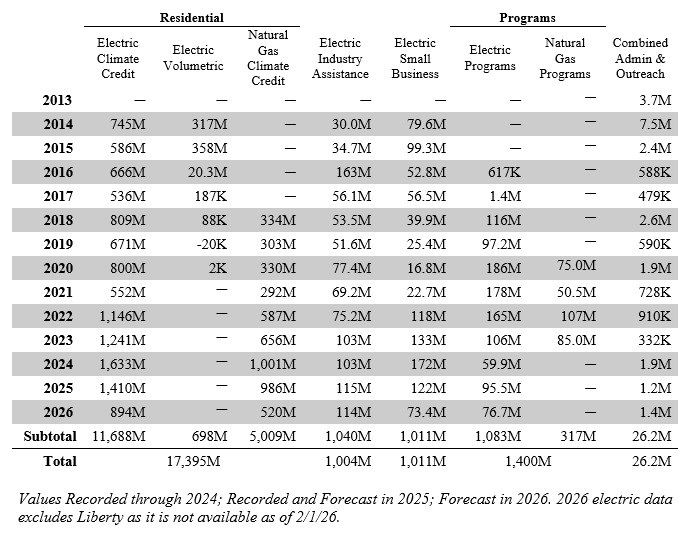
*Note: 1,000M = 1B. The volumetric portion of the residential credit was discontinued in 2015; proceeds were absorbed into the flat (per-household) residential California Climate Credit. Minor trailing amounts for the volumetric credit in subsequent years represent bill disputes and account settlements between IOUs and individual customers; table does not track residential volumetric after 2020.
More information on other CPUC Programs that Address Climate Change
The Cap-and-Invest Program is only one piece of California's work to address climate change. At the CPUC:
- We're administering an integrated resource planning process designed to ensure the electric sector is on track to help California achieve its statewide 2030 GHG reduction target at least cost while maintaining electric service reliability.
- We're increasing the amount of renewable energy that powers the grid.
- We've created ambitious energy efficiency incentive programs.
- We're making it easier for people to own and charge zero emission vehicles.
- We offer incentives for income-qualified residential and business-owned solar in disadvantaged communities and for renewable energy and energy storage for all customers.
|
Quick Reference Guide to CPUC's Cap-and-Invest Program Websites |
|
|
Go here |
To find out about… |
|
Basics and summary statistics |
|
|
Climate Credit amounts and FAQ |
|
|
Info for small business owners and FAQ |
|
|
Eligibility requirements and FAQ |
|
|
Which industries qualify as EITE |
|
|
Related CPUC documents |
|
